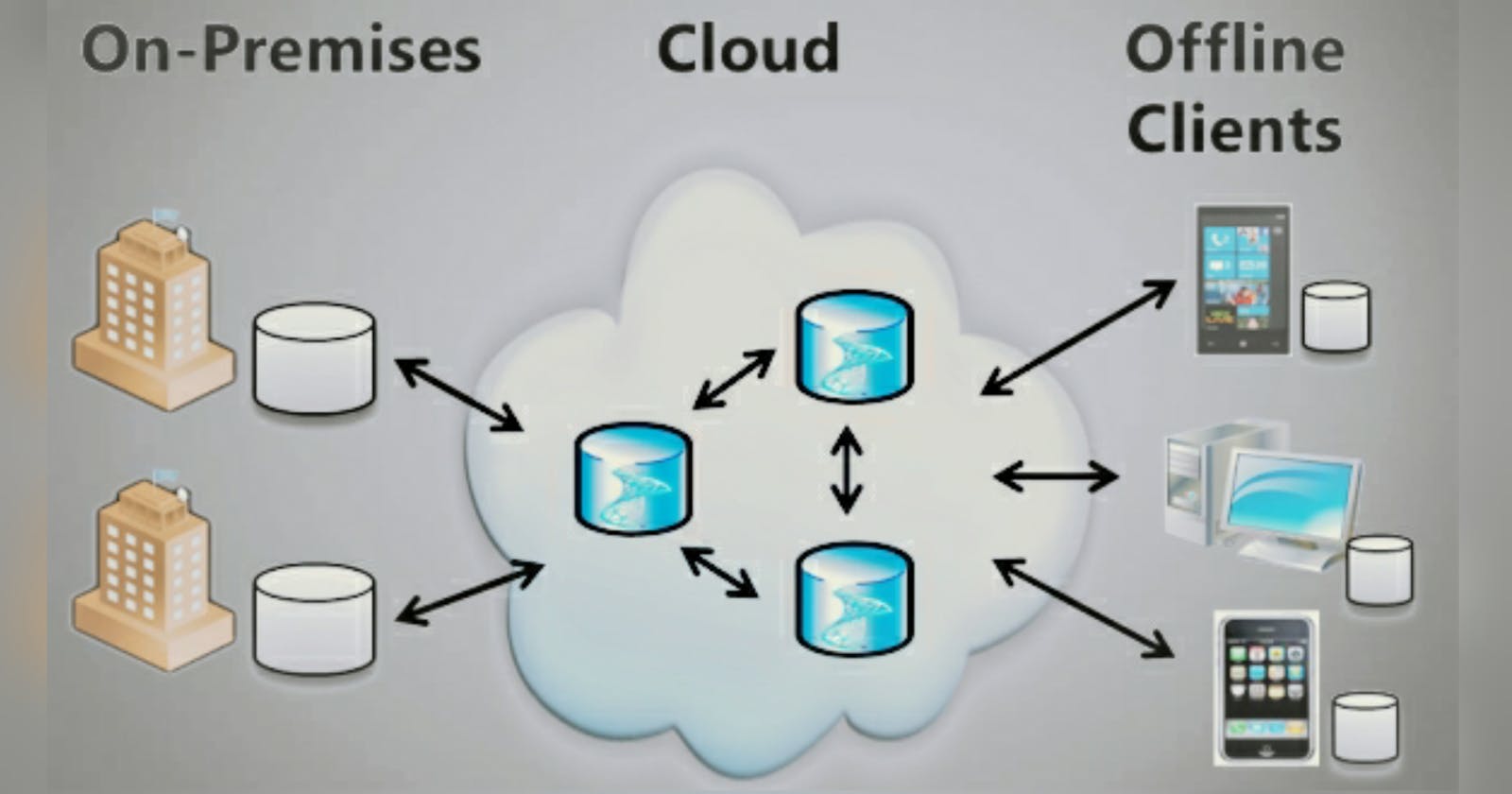
What is Cloud Data Sync?
Cloud Computing offers the possibility of synchronizing files on many devices but also of sharing them between users. Synchronization is presented as a process of matching, that is, keeping the contents of two or more storage locations identically. On the other hand, Cloud synchronization keeps the same collected file in different locations through cloud storage services. That is a fantastic way to keep files accurate, consistent, and accessible to multiple users across different locations or platforms. Cloud data synchronization is fundamental to IoT and most mobile solutions. This technical review summarizes how cloud data synchronization works, different commercial providers, and the use case of this technology.
How does Cloud Data Sync Work?
There is no one correct answer, as it will all depend on your personal Cloud syncing and cloud migration needs [1]. Synchronization can be unidirectional or bidirectional. The difference lies in the direction in which the duplication of data is done.
During a unidirectional synchronization, the duplication of the updates carried out is done in a single direction. One-way sync uploads files to the Cloud as they are modified, and users can download them manually [2].
On the other hand, during a bidirectional synchronization, the transcription of the modifications is done in both directions. With two-way sync, a cloud is intermediate storage. When altered files are uploaded, all clients download them automatically [2]. Most public services or cloud providers like Google Drive or Amazon Web Services (AWS) are based on bidirectional synchronization.
Synchronize your data in real-time
Real-time synchronization can be challenging. The complexity of sync varies widely depending on the use case [3]. For example, the amount of data, data changes, synchronous/asynchronous sync, the number of devices (connections), and what kind of client-server or peer-to-peer setup is needed affect the complexity [3]. Two solutions can ease real-time data synchronization: web applications and synchronization software or desktop application.
Usually, web applications for synchronizing data are included in cloud synchronization services. These applications match data in the Cloud with devices connected to the Internet when changes to shared data are saved there. Changes to a file in a folder are automatically saved, and updates to other equipment are also made. Access to shared data in the Cloud is possible even with a mobile phone, and various applications will read it on the web.
As for desktop applications, all you have to do is install the software that will synchronize files locally or on another private network. Those software applications are not all chargeable. Some are distributed under a “Shareware and Freeware” license. Usually, this software allows you to keep multiple versions of replaced files, set a schedule for file synchronization, compress, or encrypt files. But they also offer the possibility of synchronizing data with external hard drives, servers, and the FTP site.
Commercial Applications for Cloud Data Synchronization
Among the current cloud sync applications on the market, we have AWS DataSync, an online data transfer service that simplifies, automates, and accelerates moving data between on-premises storage systems and AWS Storage services and between AWS Storage services [4]. DataSync provides end-to-end security such as encryption of data-in-transit and data integrity verification. By moving your data with DataSync, you Pay only for the amount of data you migrate based on a flat, per-gigabyte according to your region [5]. For the US East (Ohio) region, the fee for data copied is $0.0125 per gigabyte (GB).
Microsoft Azure has its cloud data sync tool called SQL Data Sync, a service built on Azure SQL Database that lets you synchronize the data you select bi-directionally across multiple databases, both on-premises and in the Cloud [6]. It leveraged a hub and spoke architecture to synchronize data. Data Sync tracks changes using insert, update, and delete triggers. The changes are recorded in a side table in the user database [6].
Data syncing is crucial for IoT devices. How can programmers ensure that IoT devices and apps share data effectively in real-time? [7]. Developers write programs to collect data from IoT devices and push them to the Cloud. But the complexity of this process is because the more devices you have on your network, the greater the difficulty of keeping them synced [7]. Some cloud providers like AWS try to remediate this issue with services like AWS IoT Core. It lets you connect IoT devices to the AWS cloud without providing or managing servers [8]. This serverless service allows you to scale your device fleets quickly and reliably.
Future
A Cloud data synchronization is a solution that allows a large volume of files to be stored safely and securely. The services offered by providers specializing in the Cloud make it possible to avoid financial losses or, again, the loss of time that would have been allocated to the reinstatement of strategic data. The global enterprise file synchronization and sharing market was valued at USD 5.29 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach USD 21.27 billion by 2026 and grow at a CAGR of 26.3% over the forecast period (2021-2026) [9].
References
[1] SkySync, Inc., “How Does Cloud Sync Work?” Sept. 10, 2019 [online]. Available: skysync.com/cloud-sync-syncing-cloud-storage
[2] Alexander N, “What’s the Difference Between Cloud Storage, Backup and Sync?” Oct. 12, 2016 [online]. Available: msp360.com/resources/blog/difference-betwee..
[3] ObjectBox Limited, “What is Data Synchronization + How to Keep Data in Sync,” Jan. 29, 2021
[online].
Available: objectbox.io/what-is-data-synchronization-h..
[4] Amazon Web Services, “AWS DataSync,” 2021 [online]. Available: aws.amazon.com/datasync/?whats-new-cards.so..
[5] Amazon Web Services, “AWS DataSync Pricing,” 2021 [online]. Available: aws.amazon.com/datasync/pricing
[6] Microsoft Docs, “What is SQL Data Sync for Azure?” Sept. 09, 2021 [online]. Available: docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/da..
[7] Chris Tozzi, “IoT and Data Syncing: Tips for Developers,” Sweetcode.io, 2016 [online]. Available: sweetcode.io/iot-data-syncing-tips-developers
[8] Amazon Web Services, “AWS IoT Core,” 2021 [online]. Available: aws.amazon.com/iot-core
[9] Mordor Intelligence, “ENTERPRISE FILE SYNCHRONIZATION AND SHARING (EFSS) MARKET - GROWTH, TRENDS, COVID-19 IMPACT, AND FORECASTS (2021 - 2026),” 2020 [online]. Available: mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/ent..
Thank you for your time, and I hope you enjoy the reading. Please feel free to drop any comments below.
Yvan, The Architect